About Frogs
Evolution

Imagine traveling back through time millions of years to the age of the dinosaurs. Pterodactyls glide above a soggy marsh. Nearby, a colossal 80-ton Brachiosaurus munches on a tree. On the ground at its feet, something strangely familiar hops by…a frog.
Symbols of Fertility

- The frog was the ancient Eqyptian fertility goddess and was associated with the annual flooding of the Nile River.
- Frog became the symbol for the number 100,000.
- Frog charms were used to encourage pregnancy and safe birth.
Bio-indicators
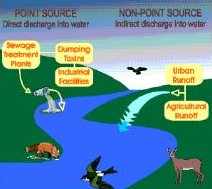
The health of frogs indicates the health of the ecosystem.
Mouths

Frogs eat live prey, insects, snails, worms, small fish. A tongue strike requires less than 1 second.
Eyes

Frogs have keen eyesight to locate prey. They see colors and in dim light. Their bulging eyes see in all directions.
Legs

Frogs can leap up to twenty times their body length, which is the same as 100 feet for a human.
Skin

Frogs get moisture through their skin. They
- don’t drink water.
- absorb oxygen through their skin, which is especially helpful underwater.
- secrete mucus to keep it moist.
- shed once a week.
Calls

Males call during mating. The calls can carry up to 1 mile. Female ears are “tuned” to species call.
True Frogs (Ranids)

Bullfrog
Green Frog
Wood Frog
S. Leopard Frog
Pickerel Frog
Tree Frogs (Hylids)

Spring Peeper
Striped Chorus Frog
Gray Tree frog
Green Tree frog
Northern Cricket Frog
Toads (Bufids)

American Toad
Fowler’s Toad
Spadefoot Toad


